Radon Gas Abatement Solutions

Radon levels often increase during colder months due to reduced ventilation and closed windows, making winter an optimal time for testing and abatement.

While radon levels can fluctuate year-round, warmer months with increased ventilation may temporarily lower radon concentrations, but testing remains essential.

Performing radon abatement during periods of stable weather can improve installation effectiveness and ensure long-term mitigation success.

Ways to make Radon Gas Abatements work in tight or awkward layouts.

Popular materials for Radon Gas Abatements and why they hold up over time.

Simple add-ons that improve Radon Gas Abatements without blowing the budget.
Radon gas abatement involves installing systems designed to reduce radon levels within buildings. These systems typically include ventilation pipes and fans that divert radon from beneath the structure to the outside atmosphere. Radon is a radioactive gas that naturally occurs from soil and rock decay, and prolonged exposure can pose health risks. Testing for radon is recommended before and after abatement to ensure levels are within safe limits. The effectiveness of mitigation measures can vary depending on seasonal conditions, soil composition, and building design.
Statistics show that radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking, with approximately 21,000 deaths annually attributed to radon exposure. The EPA recommends action if radon levels exceed 4 pCi/L. Proper timing of radon abatement can optimize results, especially when performed during seasons with stable weather conditions, minimizing the impact of environmental factors on system performance.
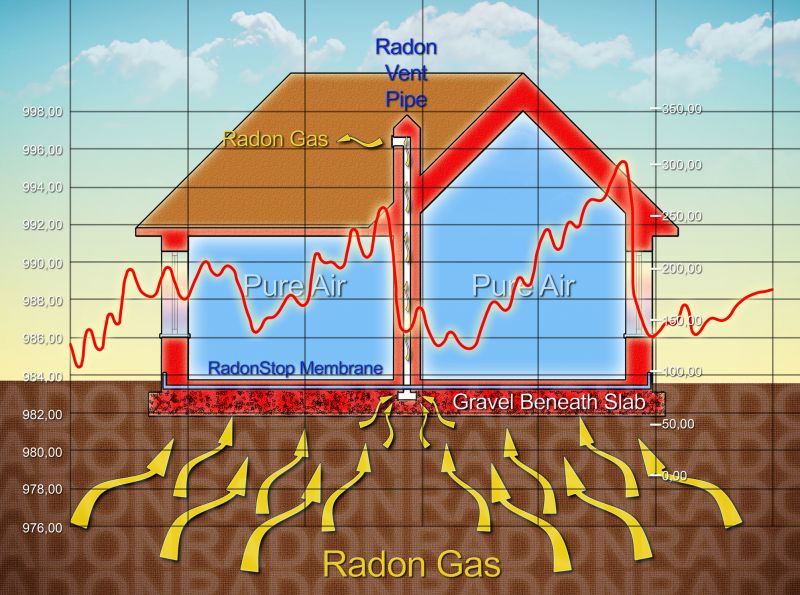
A typical radon mitigation system includes vent pipes and fans to safely vent radon outside.

Testing involves short-term or long-term detectors placed in key areas of a building.
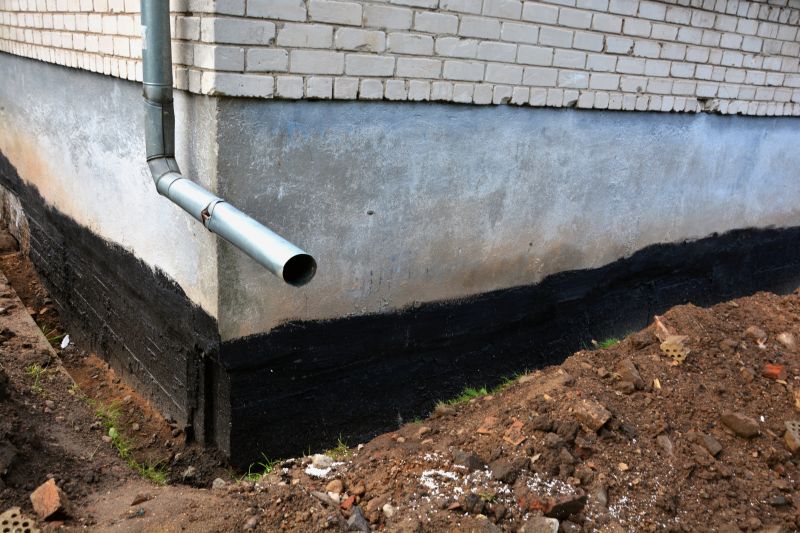

This method reduces soil gas entry by creating a vacuum beneath the foundation.

Mitigation can significantly lower radon levels, improving indoor air quality.

High-end options that actually feel worth it for Radon Gas Abatements.

Finishes and colors that play nicely with Radon Gas Abatements.

Little measurements that prevent headaches on Radon Gas Abatements day.

A 60-second routine that keeps Radon Gas Abatements looking new.

A frequent mistake in Radon Gas Abatements and how to dodge it.
| Season | Radon Level Variability |
|---|---|
| Winter | Levels tend to rise due to closed windows and heating |
| Spring | Levels may fluctuate with increased ventilation |
| Summer | Potentially lower levels with open windows and fans |
| Fall | Levels can increase as heating begins and windows close |
| Optimal Time | During stable weather with minimal environmental fluctuations |
Small tweaks to make Radon Gas Abatements safer and easier to use.
Lower-waste or water-saving choices for Radon Gas Abatements.
The short, realistic tool list for quality Radon Gas Abatements.
